Fields of digital innovation: analytics & data management - III
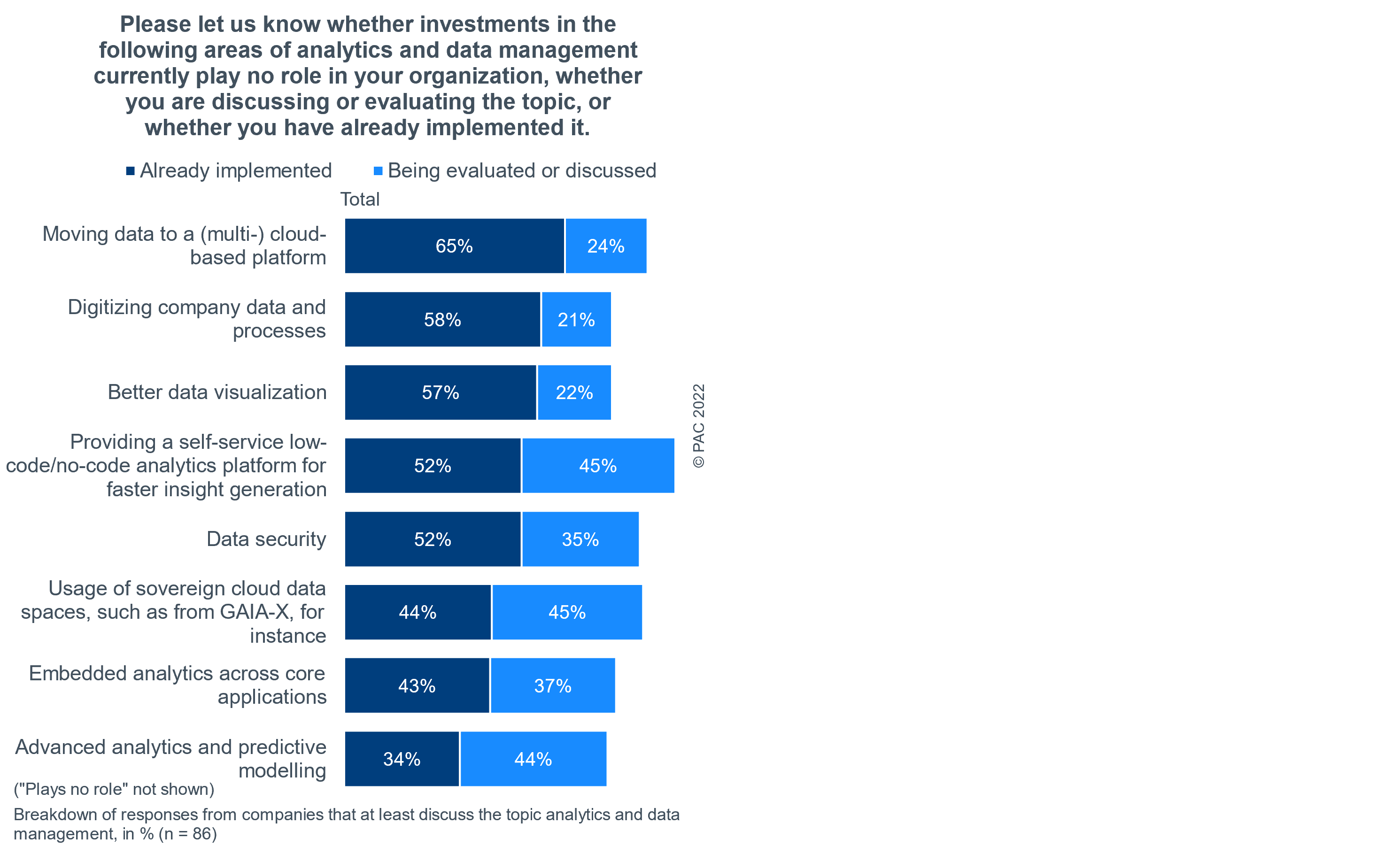
As our survey has shown, organizations continue to invest in digital innovation to improve products and services, customer service and support, as well as organizational agility and efficiency, and supply chain transparency. As data is at the heart of any digital transformation, better use of data is the most frequently stated goal of digital innovation, therefore digitizing company data and processes is a major investment area.
Moreover, analytics and data management are key for the definition, monitoring, and reporting of corporate social responsibility and ecological sustainability targets. New technologies help to analyze large amounts of data from various sources, achieve efficiency in processes related to supply chains or production and operation, and therefore allow organizations to reduce their energy and resource consumption – relevant targets not only in the current environment.
Despite its potential, big data can be rather overwhelming due to data overflow coming from multiple sources, such as social networks, the Internet, mobile phones, machines, and other devices. This endless influx of data might put significant strain on companies’ storage and compute capabilities. Cloud platforms promise scalable and efficient infrastructures and an easier handling of big data. Our survey confirms that public cloud is not only considered as a major software development and hosting platform, but increasingly also as a launching ramp for innovation. That is why more and more data has been moved to (multi-)cloud platforms, cloud-based data lakes, and data warehouses.
Data scientists and application developers can use Infrastructure/Platform-as-a-Service (IaaS/PaaS) solutions, which offer them an environment for designing innovative analytics applications, but also an increasingly broad spectrum of cloud analytics applications, up to ready-to-use algorithms that can be embedded in their own applications. Software and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions not only offer dedicated big data analytics applications; advanced analytics functions are also increasingly embedded in core applications such as ERP, CX, and HCM.
In a digitized organization, the development of basic skills in the handling of data, from collection, adaptation, and analysis, to evaluation, visualization, and “storytelling”, is key. However, dedicated skills are rare, and training measures tie up resources – and might not reach all employees to the same extent. Therefore, providing a self-service low-code/no-code analytics platform for faster insight generation is considered as particularly useful in supporting the development of a necessary “data culture” via the provisioning of easy-to-use and efficient solutions for better data visualization, irrespective of specific analytics skills. More than half of respondents have already implemented such platforms, the other half are considering it.
While in the past, traditional business intelligence addressed the exploration and reporting of historical data, the focus has shifted to the support of instant decision-making based on real-time analytics. This focus is increasingly being extended to predictive modeling, i.e. the application of statistical methods, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to historical and real-time data for forecasts related to areas such as customer behavior, capacity utilization, predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and the simulation of business decisions.
Digitized and data-driven businesses are increasingly exposed to cyberattacks. For this reason, data security has to be an integral part of any data culture. What’s more, the various recent crises have led to an increase in cyberattacks and have consequently increased awareness for cyber-security-related investments. Data security has been very high on the agenda of most decision-makers, given the enormous increase in data volumes and their importance for digitized organizations, in addition to increasing regulatory requirements in Europe and in many sectors.
Analytics and data management not only directly address better use of data, the most frequently stated goal of digital innovation in our survey; they also provide an important basis for a range of other digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, augmented and virtual reality, Internet of Things, and future quantum computing usage – these topics will be discussed separately.
0 thoughts on "Fields of digital innovation: analytics & data management – III"